
Posted: November 13, 2020
Scientists believe that the first known cells originated on Earth around 3.8 billion years ago! These were prokaryotes – single celled organisms without a nucleus. There are 200 different types

Posted: November 6, 2020
You may have enjoyed taking medicine more if you had lived centuries ago. As far back as the 9th century, sugar was given as a medicine, a practice which continued

Posted: October 30, 2020
Ever heard the phrase “blowing hot and cold? Did you know that it may have originated from one of Aesop’s fables. He was a Greek slave and storyteller from between
Posted: October 23, 2020
Microscopes have been around for hundreds of years, with the earliest known as “flea glasses” because they were used to observe insects. Before they were invented, people believed that illnesses

Posted: October 9, 2020
The study of genetics is fascinating. Did you know that genes can break or disappear!! Most mammals, due to a particular combination of genes, have the ability to produce their

Posted: October 2, 2020
DNA contains the genetic instructions for the development and functioning of a living organism. Here are some amazing facts about DNA and genetics. You are not 100% human!! Around 5-8%

Posted: September 25, 2020
There are many transition metals, with many different uses. One of these metals is zinc. Zinc is useful in a number of different ways. Medical studies have found that using

Posted: September 11, 2020
If you don’t like learning about fractions, you would have been happy in Maths lessons centuries ago! Fractions as we use them today did not exist in Europe until the

Posted: September 4, 2020
Did you know that the blood of different animals can be different colours. The different colours are caused by pigments and proteins found in the blood, which help the animals
Posted: August 28, 2020
The brain is part of your body’s central nervous system. It’s the most complicated part of your body. The brain is an incredible organ which has the ability to send
Posted: August 21, 2020
Oxygen is the third most abundant element in the universe. It is made in stars which are 5 or more times heavier than the Sun, when they burn helium and

Posted: August 14, 2020
Hydrogen is believed to be one of three elements produced in the Big Bang, alongside helium and lithium. Most of the energy on our planet is due to hydrogen. This
Posted: August 7, 2020
The rhombicosidodecahedron, or small rhombicosidodecahedron, is known as an Archimedean solid. It is one of thirteen convex solids made of two or more types of regular polygon faces. Polygons are

Posted: July 31, 2020
Salt is incredibly important, and really useful. A common myth is that Roman soldiers were partly paid in salt, resulting in the word “salary” We need to keep levels of
Posted: July 24, 2020
When you get into the bath, the water level goes up – you would expect it to. But if you pour a handful of salt (for example sodium chloride) into

Posted: July 17, 2020
If you jump out of a plane, you will accelerate towards the Earth for a while. The speed at which you fall will eventually even out as a result of

Posted: July 10, 2020
Apparently most people’s favourite number is 7! Seven does have many familiar connections. There are seven days in the week and seven wonders of the world, seven colours of the

Posted: July 3, 2020
If you enter Pi to two decimal places (3.14) in your calculator and look at it in the mirror, you’ll see it spells ‘pie’. Grab yourself a piece of pie

Posted: June 26, 2020
Cheetahs are the fastest animal on land. They can accelerate from standing still to over 60 mph in just 3 seconds, and can reach speeds of up to 75 mph.

Posted: June 19, 2020
Electrolysis can be used to extract lead from molten lead bromide, but did you know some of these interesting facts about lead? Ancient Romans used lead for making pipes. The

Posted: June 12, 2020
The oddly “clean” smell that sometimes comes during a storm is that of ozone!! Lightning strikes split diatomic oxygen molecules in the atmosphere into individual oxygen atoms. These can then combine with
Posted: June 5, 2020
Tardigrades are eight-legged animals that are nicknamed water bears. They are tiny, up to 1.2mm long, but are capable of withstanding the most extreme environments. These hardy creatures survive even

Posted: May 29, 2020
The Golden Ratio is a special number describing a ratio of approximately 1 to 1.618 that is commonly found in nature. It appears many times in geometry, art, architecture and other

Posted: May 22, 2020
Planet Earth is sometimes referred to as the blue planet because it is mostly covered in oceans and has a thick atmosphere, giving it a blue appearance. Mars, however, is

Posted: May 15, 2020
Sequences can be really useful. Special algorithms use the data of past crimes to try and predict when and where crime may occur in the future. In Los Angeles using

Posted: May 8, 2020
Did you know that eleven plus two is actually an anagram of twelve plus one. This is very apt, as the answer to both is 13!! To make it more
Posted: May 5, 2020
Did you know that the equals sign (=) was invented in 1557 by a Welsh mathematician named Robert Recorde? However it was not widely used until the 1700’s. The symbols
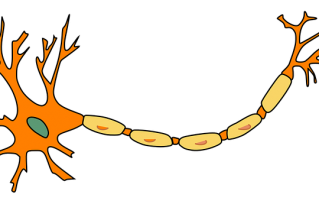
Posted: May 1, 2020
The speed of nerve impulses varies enormously in different types of neurone. The fastest travel at about 250 mph, faster than a Formula 1 racing car! The nervous system is made

Posted: April 28, 2020
Our reaction time is the time it takes for us to respond to something happening. In this time, our senses notice something and send a signal back to the brain,
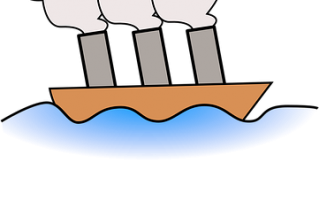
Posted: April 24, 2020
You probably already know that objects float because they are less dense than water. But have you ever wondered how huge objects like ships, don’t sink? They float, even though

Posted: April 23, 2020
Avogadro’s constant is a massive number, and can be really difficult to comprehend when you are completing calculations with moles. Imagine this: • If there were a mole of rice

Posted: April 21, 2020
In about 24o BC Eratosthenes, an ancient Greek scientist, measured the Sun’s angle at two places. Using trigonometry he calculated the Earth’s radius. Legend also has it, that Eratosthenes went blind

Posted: April 17, 2020
Archimedes is well known for discovering that when you enter into a bath, the water level immediately rises. He noticed that the weight of his body displaced a certain amount
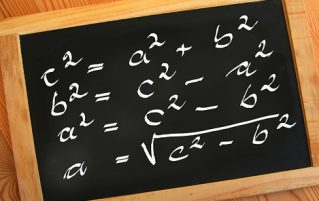
Posted: April 16, 2020
You have probably all heard of Pythagoras, and his theorem, but what do you know about the man himself? Pythagoras was an Ancient Greek mathematician and philosopher. Not much accurate information

Posted: April 14, 2020
Sequences are everywhere! The Fibonacci sequence is found in many places in nature. It is a series of numbers in which the next number is calculated by adding the previous

Posted: April 10, 2020
Did you know that the earliest microscopes were known as “flea glasses” because they were used to study small insects? Or that most of the oxygen produced by photosynthesis doesn’t

Posted: April 7, 2020
Helium is one of the noble gases and the second most abundant element in the universe. It is so light that Earth’s gravity is not strong enough to hold on

Posted: April 3, 2020
Unfortunately for slugs, their moist skin is far more permeable to water than the skin of most other animals. When salt is placed on them the process of osmosis begins
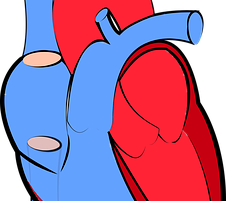
Posted: April 2, 2020
Your heart is an amazing organ. It will beat about 115,000 times each day, and pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood every day. It can even continue beating when it’s disconnected

Posted: March 27, 2020
There are many amazing facts about water. Did you know for example that: Goldfish remember things better in cold water than in warm water There are more atoms in a
